サーバー統合ドキュメント
製品通信プロセス
通常プロセス
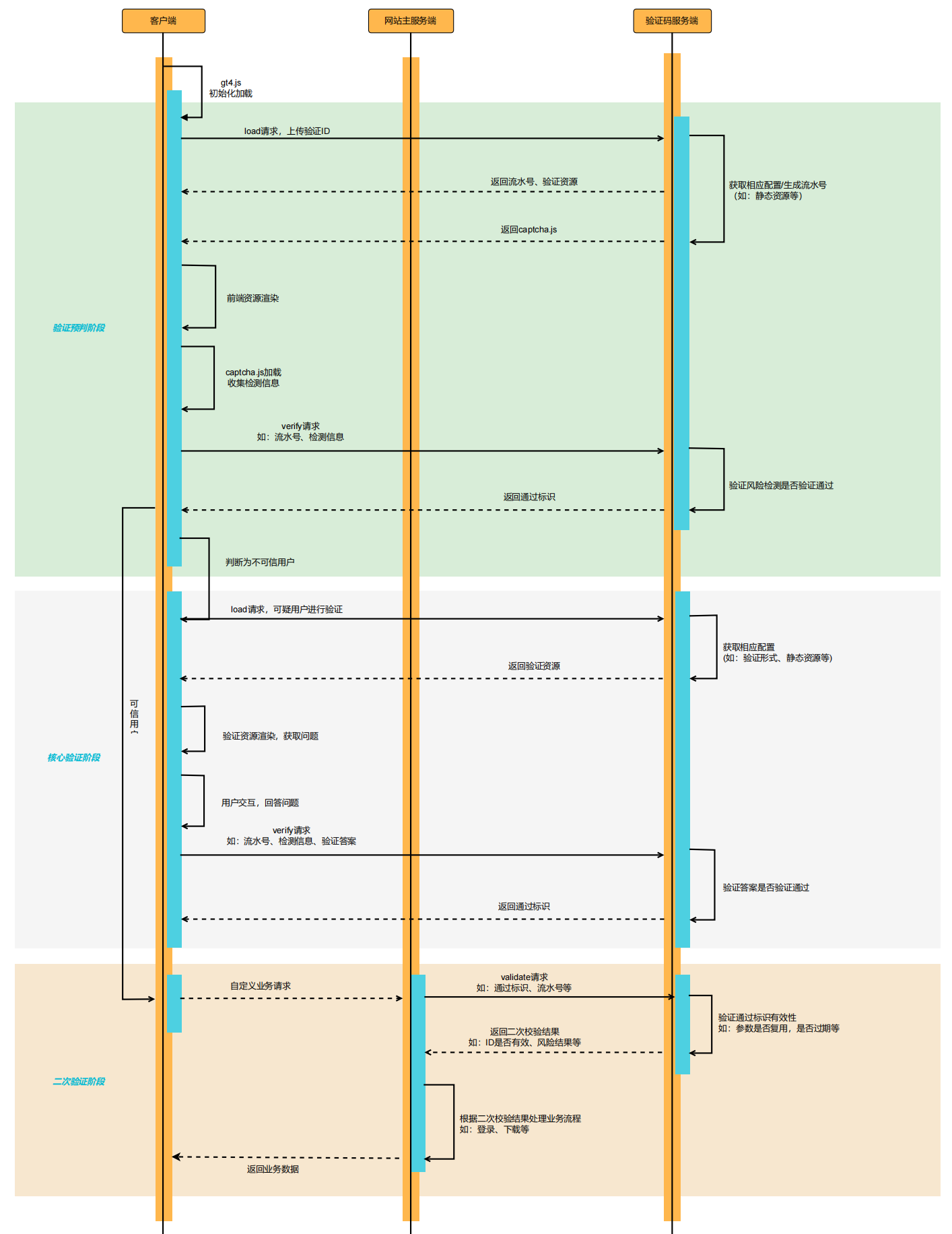
認証サービスが正常で、ユーザーのネットワークが正常にロードされる場合、キャプチャプロセスが進行します。サーバーは二次認証フェーズに重点を置く必要があります。
異常プロセス
キャプチャオフラインプロセス
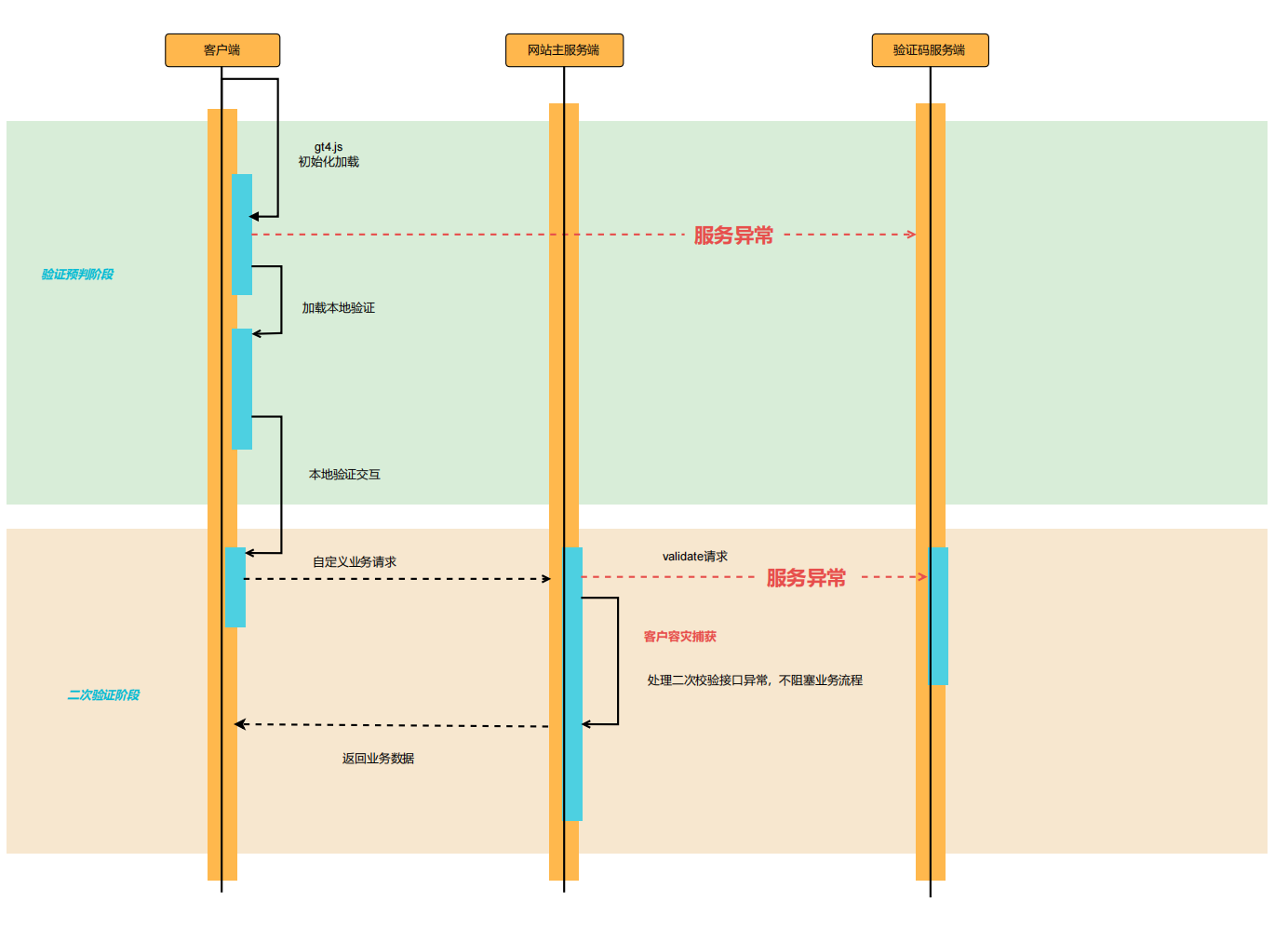
認証サービスが異常でキャプチャのオフラインモードが使用される場合、サーバーは二次認証フェーズに重点を置く必要があります。この場合、サーバーがキャプチャサービスにリクエストを送信すると例外が発生します。例外をキャッチし、ビジネスシナリオに基づいてユーザーの進行を許可するかどうかを決定することをお勧めします。
カスタムダウングレードプロセス(参考用)
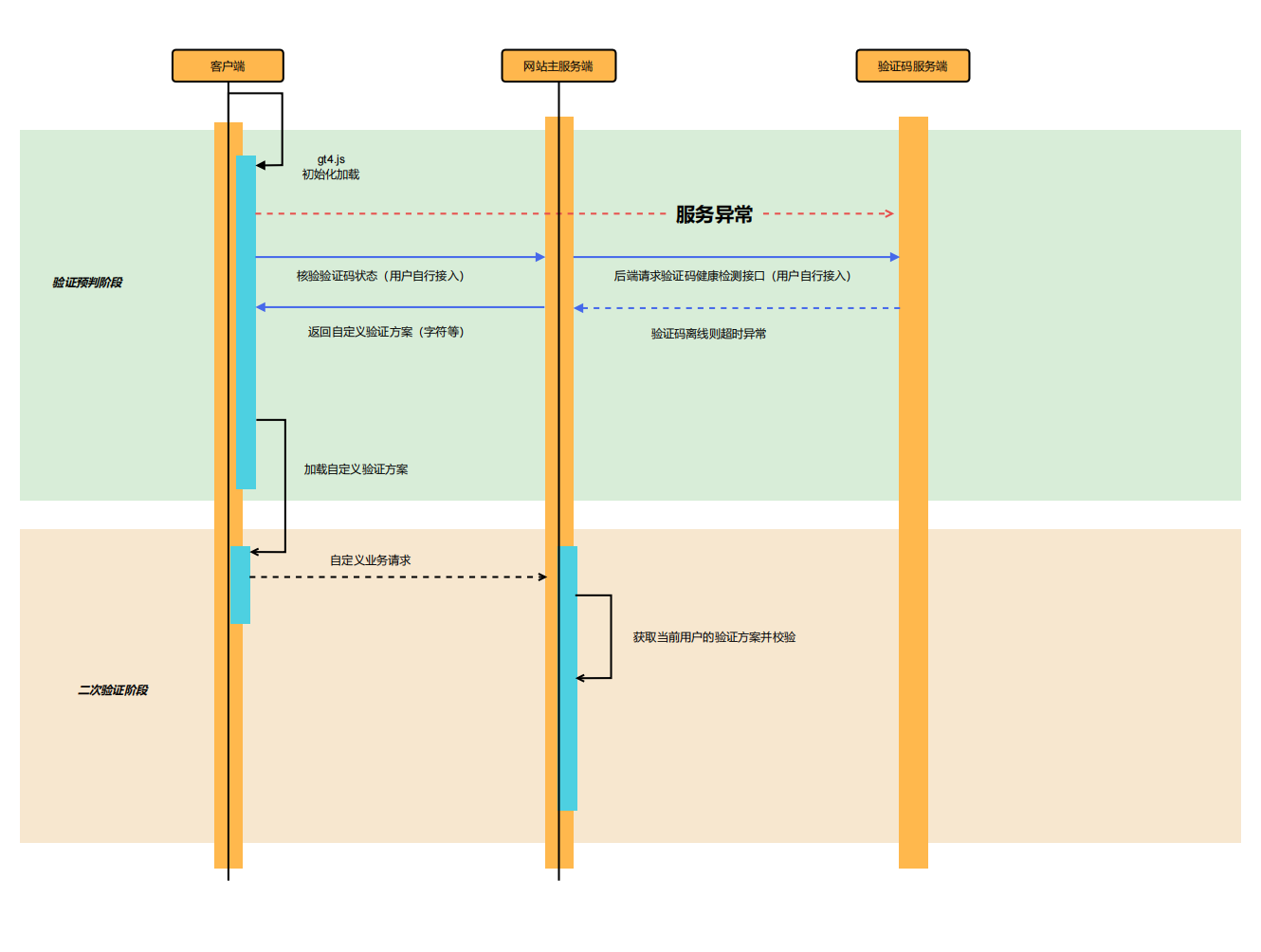
認証サービスが異常で、文字認証などのカスタムダウングレード認証が使用される場合、サーバーはフロントエンドが特定の認証方法を判断できるようにインターフェースまたはスイッチを追加することをお勧めします。サーバーはキャプチャが正常に機能しているかどうかを判断するために、キャプチャが提供するcheck_statusインターフェースを使用できます。
サーバー側キャプチャ統合プラン
統合前の準備
統合クライアントから必要なリソース、ドメインアドレス、その他の情報を取得します。デプロイ後、内部会社の連絡担当者に連絡してこの情報を取得してください。
| クライアントタイプ | 必要なリソース | リソースの説明 | サーバー | captchaId | 認証シナリオID、管理コンソールで作成可能 |
| captchaKey | 認証シナリオKEY、新しいシナリオを管理コンソールで作成する際に生成され、captchaIdと1対1で対応 |
サーバー統合
ユーザーがフロントエンドインターフェースでキャプチャを通過すると、キャプチャ関連のパラメータセットが生成されます。ユーザーのビジネスリクエストにはこれらのパラメータが含まれ、バックエンドビジネスインターフェースはこれらのパラメータをEngageLabの二次認証インターフェースにアップロードして、ユーザーの認証の有効性を確認します。
ログインシナリオを例に取ると:
- キャプチャを統合する前、フロントエンドはユーザー名とパスワードをビジネスログインインターフェースに送信します。ビジネス側はユーザー名とパスワードが一致するかどうかを確認します。一致すればユーザーはログインし、一致しなければログインは拒否されます。
- キャプチャを統合した後、フロントエンドはビジネス情報とキャプチャ関連パラメータをビジネスログインインターフェースに送信します。ビジネス側はキャプチャ関連パラメータをキャプチャサーバーの二次認証(validate)インターフェースに送信してキャプチャ結果を取得します。キャプチャ結果とユーザー名およびパスワードの一致結果に基づいて、ユーザーが次のビジネスプロセスに進むことを許可するかどうかを判断します。
validateインターフェースの説明
| インターフェース情報 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| インターフェースアドレス | https://captcha-api.engagelab.com/validate |
| リクエスト方法 | POST |
| リクエスト形式 | application/json |
| レスポンスタイプ | json |
リクエストパラメータ
| パラメータ名 | 型 | 説明 | 出所 |
|---|---|---|---|
| lot_number | string | サーバー認証ID | フロントエンドによって提供される |
| captcha_output | string | 認証出力 | フロントエンドによって提供される |
| pass_token | string | 認証パストークン | フロントエンドによって提供される |
| gen_time | string | 認証タイムスタンプ | フロントエンドによって提供される |
| captcha_id | string | 認証シナリオID | ビジネス設定ファイル、フロントエンドで使用されるcaptchaIdと一致する必要あり |
| sign_token | string | 認証署名 | ビジネス側によって生成される |
sign_tokenは以下のように生成されます:
現在の認証のlot_numberを元のメッセージとして使用し、顧客のプライベートキーcaptchaKeyをキーとして使用し、hmac_sha256ハッシュアルゴリズムを適用してメッセージとキーの一方向ハッシュを実行し、最終署名を生成します。
以下のJavaコードはプロセスを示しています:
String signToken = new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_SHA_256, captchaKey).hmacHex(lotNumber);
リクエストボディの例
{
"lot_number": "f26d13345c9980c7705b9111b9398a0f",
"captcha_id": "59bbe0f128f0624fdd185a6a2207aa54",
"sign_token": "2e61e2f6d40e2896b18978fe6ae1416347fc43027ab7c875460d17ffa149dd7a",
"pass_token": "79a4b7fc89d917b346d35286991bc9bca388a78bd31c20fa00907dcb8632611c",
"gen_time": "1684826917",
"captcha_output": "X4oDQ5p61MhE0Zpy5wQcl98WjrDdlDyL5B_VO0zPYnS9ITuz1ZZ6o0iw4Odk9f0AbAlzraqmeLGSmQWHPwJr2Vvf_Nm2Z0SMCn2ATME67e5UhMdopMgc8_zZi-SFRyH1"
}
レスポンスパラメータ
| パラメータ名 | 型 | 必須 | 例 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| status | String | はい | success | レスポンスステータス、successは正常応答を示す |
| data | Object | はい | データフィールドを参照 | インターフェースが正常応答時に返される |
dataフィールドの説明は以下の通りです:
| パラメータ名 | 型 | 必須 | 例 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| result | String | はい | success | 二次認証結果、successは認証成功、その他の値は認証失敗を示す |
| reason | String | はい | "" | 認証結果の説明 |
| captcha_args | Object | はい | {} | クライアントに返される情報、主に戦略結果を含む |
キャプチャ認証成功の指標は:レスポンスのstatusフィールドがsuccessであり、かつresultフィールドもsuccessであること
captcha_argsフィールドには以下のパラメータが含まれます:
| パラメータ名 | 型 | 必須 | 例 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| model_cnn | int | はい | 0 | CNNスライディングトラックモデルの判定結果、0は正常トラック、1は異常トラックを示す |
| model_probability | int | はい | 0 | キャプチャプラットフォームリクエストかどうか、0は正常ユーザー、1はキャプチャリクエスト ビジネス側でのリアルタイム処理を推奨 |
| used_type | String | はい | slide | 今回使用された認証方法 |
| web_simulator | int | はい | 0 | シミュレーターかどうか、0は正常ブラウザ、1はシミュレーターを示す |
| user_ip | String | はい | "127.0.0.1" | 認証成功時のユーザーIP |
| user_referer | String | はい | "" | 認証成功時のユーザーリクエストのリファラー |
| cnn_records | int | はい | 0 | プロセス中にスライディングモデルが異常トラックを予測したかどうか |
| user_agent | String | はい | "User-Agent" | 認証成功時のユーザーUA |
| lot_number | String | はい | "9b57c5289e" | ユーザー認証ID |
注意:model_probabilityはキャプチャ指標です。この指標が1の場合、異常なキャプチャリクエストとして識別されます。ビジネス側での後続処理を推奨します。
data内のresultフィールドがsuccessの場合、認証結果が成功であることを示します
レスポンス例
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"captcha_args": {
"cnn_records": 0,
"lot_number": "a989b864ad08cc08f270c22d9ab1fba0",
"model_cnn": 0,
"model_probability": 0,
"used_type": "slide",
"user_agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/135.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"user_ip": "59.174.224.96",
"user_referer": "http://127.0.0.1:5000/",
"web_simulator": 0
},
"reason": "validate success",
"result": "success"
}
}
Javaコード統合例
Java言語を使用したビジネスサイドの開発を例に取ると、参照コードは以下の通りです:
package com.engagelab.demo.controller;
import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.HmacAlgorithms;
import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.HmacUtils;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import org.springframework.http.*;
import org.springframework.http.client.SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory;
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class MainController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String userLogin(@RequestParam Map<String, String> getParams) {
// 1. パラメータ情報を初期化します。これはフロントエンドで使用されるcaptchaIdと一致させる必要があり、設定ファイルに配置することもできます。
String captchaId = "37830cbb24f5a2134d39c7cf3093bc14";
String captchaKey = "ab8aeb88a3c30e170ab04af8ada6e6ec";
// domainはEngageLabのキャプチャサービスドメインです
String domain = "https://captcha-api.engagelab.com";
// 2. 検証後にフロントエンドから渡される検証パラメータを取得します
String lotNumber = getParams.get("lot_number");
String captchaOutput = getParams.get("captcha_output");
String passToken = getParams.get("pass_token");
String genTime = getParams.get("gen_time");
// 3. 署名を生成します
// 標準的なHMACアルゴリズムを使用して署名を生成し、ユーザーの現在の検証シリアル番号lot_numberを元のメッセージとして、クライアントの検証秘密鍵をキーとして使用します。
// SHA256ハッシュアルゴリズムを使用して、メッセージとキーを一方向にハッシュ化し、最終的な署名を生成します。
String signToken = new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_SHA_256, captchaKey).hmacHex(lotNumber);
// 4. 検証パラメータをEngageLabの二次検証インターフェースにアップロードし、ユーザーの検証ステータスを確認します。
Map<String, String> queryParams = new HashMap<>();
queryParams.put("captcha_id", captchaId);
queryParams.put("lot_number", lotNumber);
queryParams.put("captcha_output", captchaOutput);
queryParams.put("pass_token", passToken);
queryParams.put("gen_time", genTime);
queryParams.put("sign_token", signToken);
String url = String.format(domain + "/validate");
SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory clientHttpRequestFactory = new SimpleClientHttpRequestFactory();
clientHttpRequestFactory.setConnectTimeout(3000); // 接続タイムアウトを設定
clientHttpRequestFactory.setReadTimeout(1500); // 読み取りタイムアウトを設定
RestTemplate client = new RestTemplate();
client.setRequestFactory(clientHttpRequestFactory);
JSONObject responseJsonObject = new JSONObject();
// インターフェース例外に注意し、二次検証インターフェースの例外や応答ステータスが200でない場合に対応する例外処理を行います。
// インターフェースリクエストのタイムアウトやサーバーが応答しないためにビジネスプロセスが妨げられないようにします。
try {
RequestEntity<Map<String, String>> requestEntity = RequestEntity.post(url).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(queryParams);
ResponseEntity<String> response = client.exchange(requestEntity, String.class);
String resBody = response.getBody();
responseJsonObject = new JSONObject(resBody);
}catch (Exception e){
// Todo: インターフェースアクセスのタイムアウトの場合を処理します。このデモでは、デフォルトで検証が成功したとみなします。
responseJsonObject.put("status", "success");
responseJsonObject.put("data", new JSONObject("{\"result\": \"success\", \"reason\": \"request captcha api fail\"}"));
}
// 5. EngageLabから返されたユーザー認証ステータスを考慮し、ウェブサイト所有者は独自のビジネスロジックに従います。
JSONObject res = new JSONObject();
// キャプチャ検証が成功する条件は:1. jsonObject内のstatusフィールドがsuccessであること、2. jsonObjectのdataフィールド内のresult属性がsuccessであること。
String status = responseJsonObject.getString("status");
if (status.equals("success")) {
String data = responseJsonObject.getJSONObject("data").getString("result");
if (data.equals("success")) {
res.put("login", "success");
res.put("reason", responseJsonObject.getJSONObject("data").getString("reason"));
} else {
res.put("login", "fail");
res.put("reason", responseJsonObject.getJSONObject("data").getString("reason"));
}
JSONObject captchaArgs = responseJsonObject.getJSONObject("data").getJSONObject("captcha_args");
// ここで、プロトコル破り認識結果を取得します。このデモでは記録するだけです。ビジネスは独自のモデルに従って処理することをお勧めします。
// model_probabilityが0の場合は通常のユーザーを示し、1の場合はプロトコル破り(インターフェースを直接アクセスするクローラー)を示します。
Integer model_probability = captchaArgs.getInt("model_probability");
System.out.println("このインターフェースのクローラー認識結果は: " + model_probability);
} else {
// インターフェースが応答したが失敗した場合、検証失敗として処理します。
res.put("login", "fail");
res.put("reason", "captcha verify fail");
}
return res.toString();
}
}
