
A customer browses your website on Monday, abandons a cart on Tuesday, opens a promotion email on Thursday, and finally makes a purchase through your app a week later.
For many retailers, these actions live in separate systems — handled by different tools, teams, and timelines. What customers experience as one journey is often managed as disconnected campaigns behind the scenes.
Retail marketing automation closes this gap by connecting customer behavior, data, and messaging into a single, scalable system. It allows retailers to move from one-off campaigns to always-on journeys driven by real-time intent.
In this guide, we’ll explore how retail marketing automation works, where it delivers the most impact, and how to choose a platform that scales with your business.
Part 1. What's Retail Marketing Automation?

Retail marketing automation is the process of using software to automate marketing efforts and workflows in the retail sector. These software automate the repetitive tasks that retailers manage manually otherwise. These tasks include SMS marketing, emails or posting content on social media.
The purpose or objective behind retail marketing is to use automation tools to deliver instant and personalized responses to customers. This communication increases customer trust, improves loyalty and drives sales.
With this automation, retailers can expect these benefits:
- Enhanced customer experience
- Improves operational efficiency
- Increase conversion and revenue.
Part 2. Why Retailers Need Marketing Automation Today?
Modern retail marketing is no longer limited by creativity — it is limited by execution.
Retailers today manage thousands or millions of customer profiles across websites, mobile apps, and offline touchpoints. Each customer expects personalized recommendations, timely reminders, and consistent experiences across channels. Delivering this manually is not just inefficient — it is impossible at scale.
Marketing automation addresses these challenges by turning customer data into action. It enables retailers to respond to behavior in real time, personalize engagement based on intent, and maintain consistency across complex journeys.
For retail teams, marketing automation is critical because it:
- Reduces reliance on manual campaign execution
- Improves targeting accuracy and message relevance
- Accelerates conversion through timely, behavior-driven engagement
- Provides clear performance data to guide optimization and investment decisions
In short, automation shifts retail marketing from reactive campaigns to always-on customer journeys.
Part 3. Key Components of Retail Marketing Automation
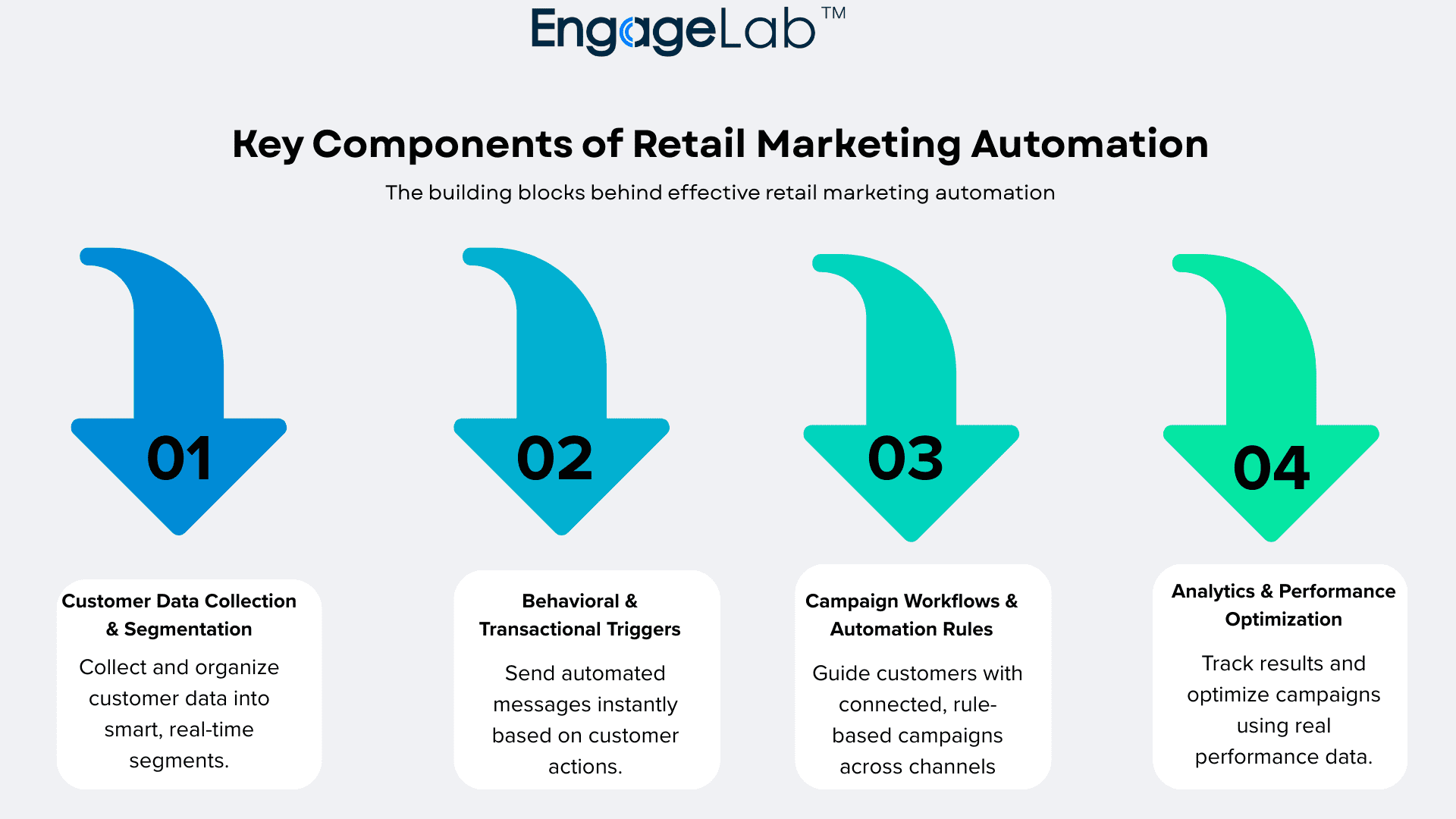
Effective retail marketing automation depends on multiple components working together to collect customer data, interpret behavior, and execute campaigns automatically.
When these elements are aligned, retailers can manage complex marketing operations without relying on constant manual effort.
Customer Data Collection and Segmentation
Customer data is the foundation of any retail automation strategy.
Automation platforms collect data across touchpoints, including purchase history, browsing behavior, and engagement across email, SMS, and messaging channels. Instead of maintaining fragmented systems, retailers can build unified customer profiles that update in real time.
Based on this data, automation tools dynamically segment customers according to behavior, preferences, and lifecycle stage. As customers interact with the brand, segments update automatically, significantly reducing campaign preparation time and manual workload for large teams.
Behavioral and Transactional Triggers
Behavioral and transactional triggers enable retailers to respond to customer actions as they happen.
These triggers initiate automated responses based on meaningful signals, such as browsing activity, cart abandonment, purchases, or account registration. Rather than relying on fixed schedules, automation ensures that communication is timely and context-aware.
Common trigger examples include:
- Cart abandonment after product browsing
- Purchase confirmation or account creation
- Product restock alerts based on prior interest
By reacting to real-time behavior, retailers can increase relevance and engagement while reducing message fatigue.
Campaign Workflows and Automation Rules
Campaign workflows define how messages are connected over time.
Automation rules guide customers through predefined journeys based on their interactions with previous messages. For example, opening an email may trigger a follow-up message, while inactivity can redirect communication to a different channel.
This rule-based orchestration ensures consistency across touchpoints and eliminates the need for manual follow-ups, allowing teams to scale communication without increasing operational complexity.
Analytics and Performance Optimization
Automation platforms provide visibility into campaign performance across channels.
Metrics such as engagement rates, conversions, and timing patterns reveal which journeys perform well and where optimization is needed. These insights allow retailers to refine messaging, adjust timing, and improve targeting based on real data rather than assumptions.
Successful retail automation relies on continuous measurement and iteration, enabling teams to scale campaigns with confidence and precision.
Part 4. Retail Marketing Campaign Automation in Practice
Retail marketing automation is most effective when it operates as a continuous system rather than a series of isolated promotions.
Instead of launching one-off campaigns, automation enables retailers to manage ongoing, behavior-driven journeys that adapt to customer actions in real time. Below are some of the most common and impactful retail automation use cases.
1. Abandoned Cart Recovery
Cart abandonment is not a single event — it is a behavioral signal.
Retail marketing automation detects abandonment in real time and initiates a sequence of actions rather than a one-off reminder. Depending on customer history, price sensitivity, and engagement patterns, the system can dynamically adjust timing, channel, and messaging.
For example:
- First-time visitors may receive a soft reminder
- Returning customers may see related product recommendations
- High-intent users can be prioritized for faster follow-up via SMS or push notifications
Once a purchase is completed, the workflow automatically stops, ensuring relevance while avoiding redundant communication. This approach maximizes recovery rates without manual intervention.
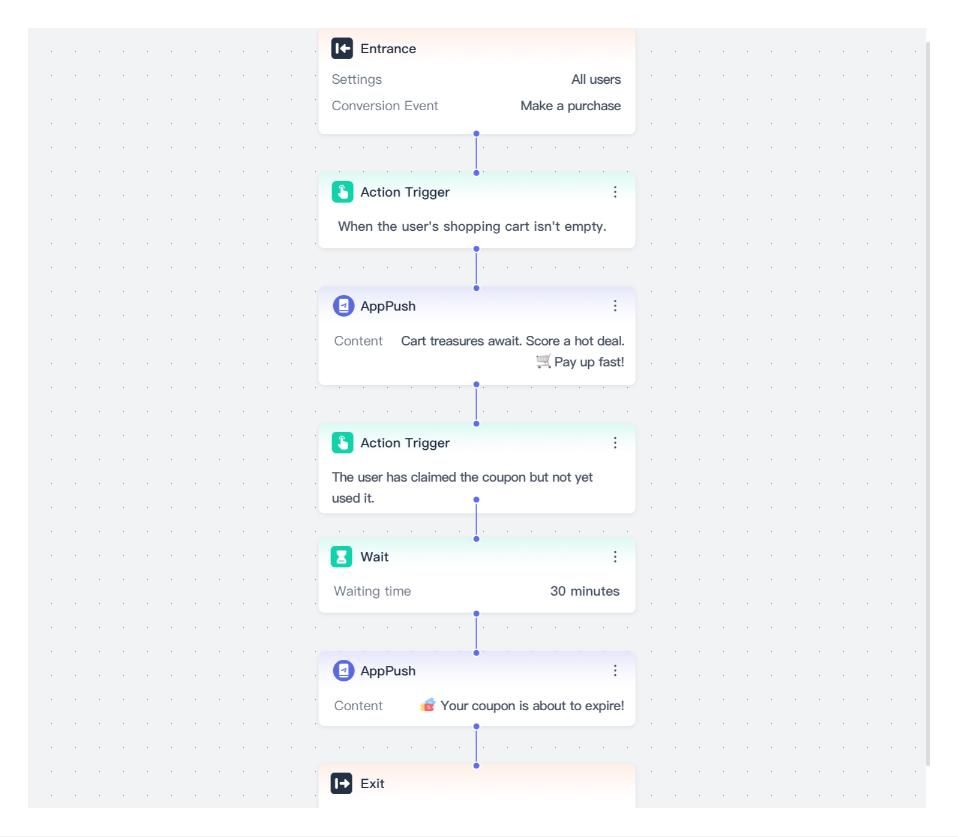
An Example of the "Abandon Cart Recovery" Process
 Sample Message
Sample Message
"Hi Alex, the items in your cart are still waiting. Complete checkout before they go out of stock."
2. Post Purchase Engagement
The customer journey does not end at checkout.
Post-purchase engagement is critical for building trust, reducing churn, and driving repeat purchases. Marketing automation enables retailers to deliver timely, context-aware communication after a transaction is completed.
Automated post-purchase workflows may include:
- Order and delivery updates
- Product usage tips or onboarding guides
- Cross-sell or replenishment reminders based on product lifecycle
Timing and relevance are key. Instead of generic follow-ups, automation uses purchase data and behavior signals to determine when and how to re-engage customers. This transforms post-purchase communication from transactional messages into long-term relationship building.
 Sample Message
Sample Message
"Hi Emma, your order has been delivered. Check this guide to get the best results from your purchase."
3. Inactive Customer Re-Engagement
Customer inactivity is a signal — not a dead end.
Retail marketing automation identifies customers who have stopped engaging based on defined inactivity thresholds.
For example:
- Customers may receive product recommendations aligned with previous purchases
- Messaging frequency and incentives can be adjusted based on engagement history
- Channels can shift dynamically to maximize reach without over-communication
By personalizing re-engagement efforts, retailers can recover dormant users more efficiently while protecting brand experience and marketing spend.
 Sample Message
Sample Message
"Hi Sarah, we noticed you have not shopped with us recently. Here are a few items picked based on your past orders."
Part 5. Choosing the Right Retail Marketing Automation Platform
As retail marketing automation becomes more complex, the platform behind it matters as much as the strategy itself.
EngageLab is built to support high-volume, omnichannel retail operations through a unified automation framework. Instead of managing disconnected tools, teams can orchestrate customer journeys across email, SMS, push notifications, and in-app messaging from a single interface.
With visual journey builders, real-time data synchronization, and behavior-driven triggers, EngageLab enables retailers to move beyond isolated campaigns toward scalable, always-on engagement. Marketing teams can test, optimize, and adapt journeys based on actual customer behavior — without engineering dependency.
For retailers operating at scale, this level of reliability, flexibility, and data consistency is what turns marketing automation from a tactical tool into a growth engine.
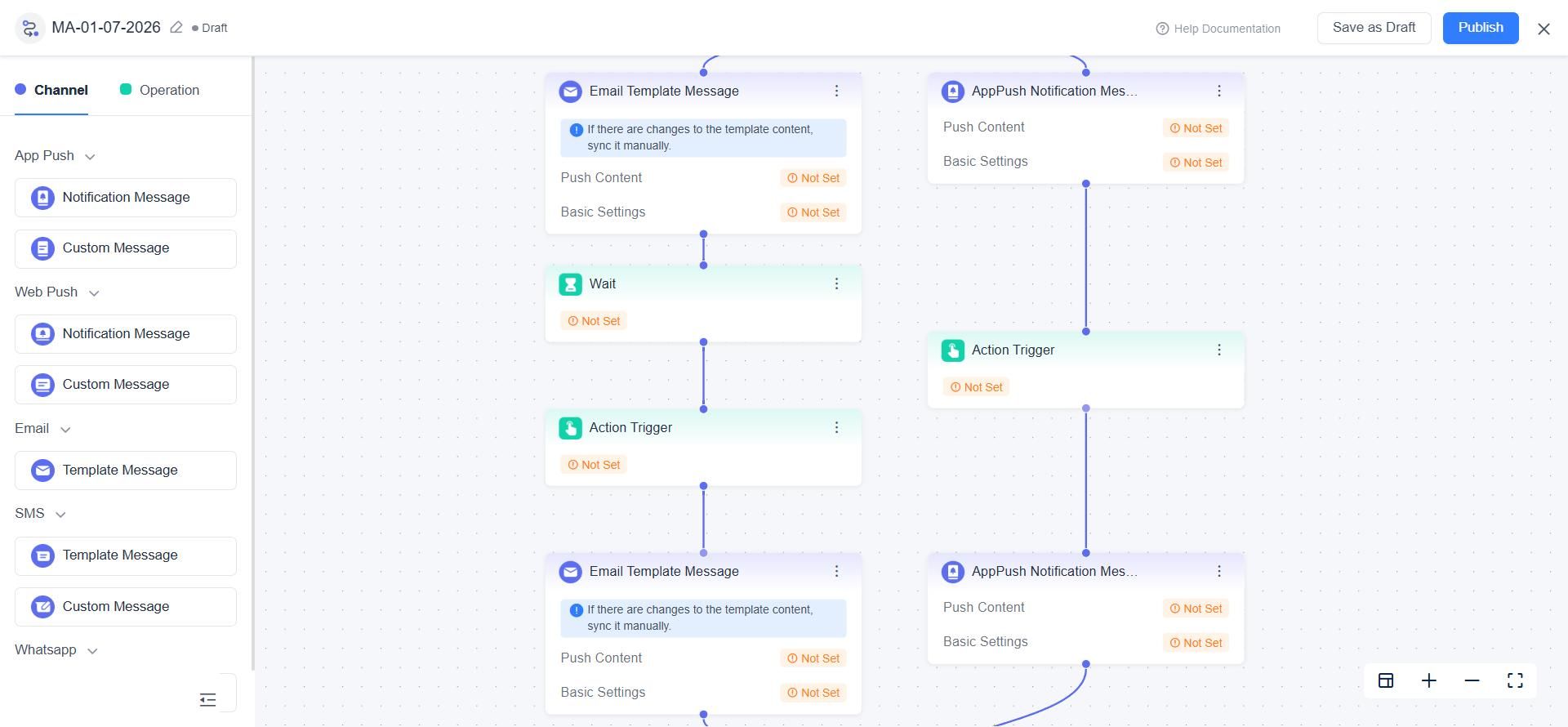
EngageLab's Visual Journey Builder
Conclusion
In a competitive retail environment, growth is no longer driven by how many campaigns you run, but by how well your systems scale.
Retail marketing automation allows teams to move beyond one-off promotions and manual workflows. By responding to customer behavior in real time and coordinating engagement across channels, retailers can increase conversion, retention, and lifetime value without adding complexity.
Platforms built for scale, such as EngageLab, play a key role in making this possible. By unifying data, journeys, and execution in one system, retailers gain the clarity and control needed to turn customer engagement into a sustainable growth engine.









